Caregiving in Australia: an overview of the role and requirements
Caregiving has become an essential profession in Australia, particularly within aged care services where dedicated support workers provide vital assistance to elderly individuals and those with disabilities. This role encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, from personal care to emotional support, requiring specific skills and qualifications. Understanding what caregiving involves, the duties expected, and the pathways to enter this rewarding field can help those considering a career in this sector make informed decisions about their professional future.
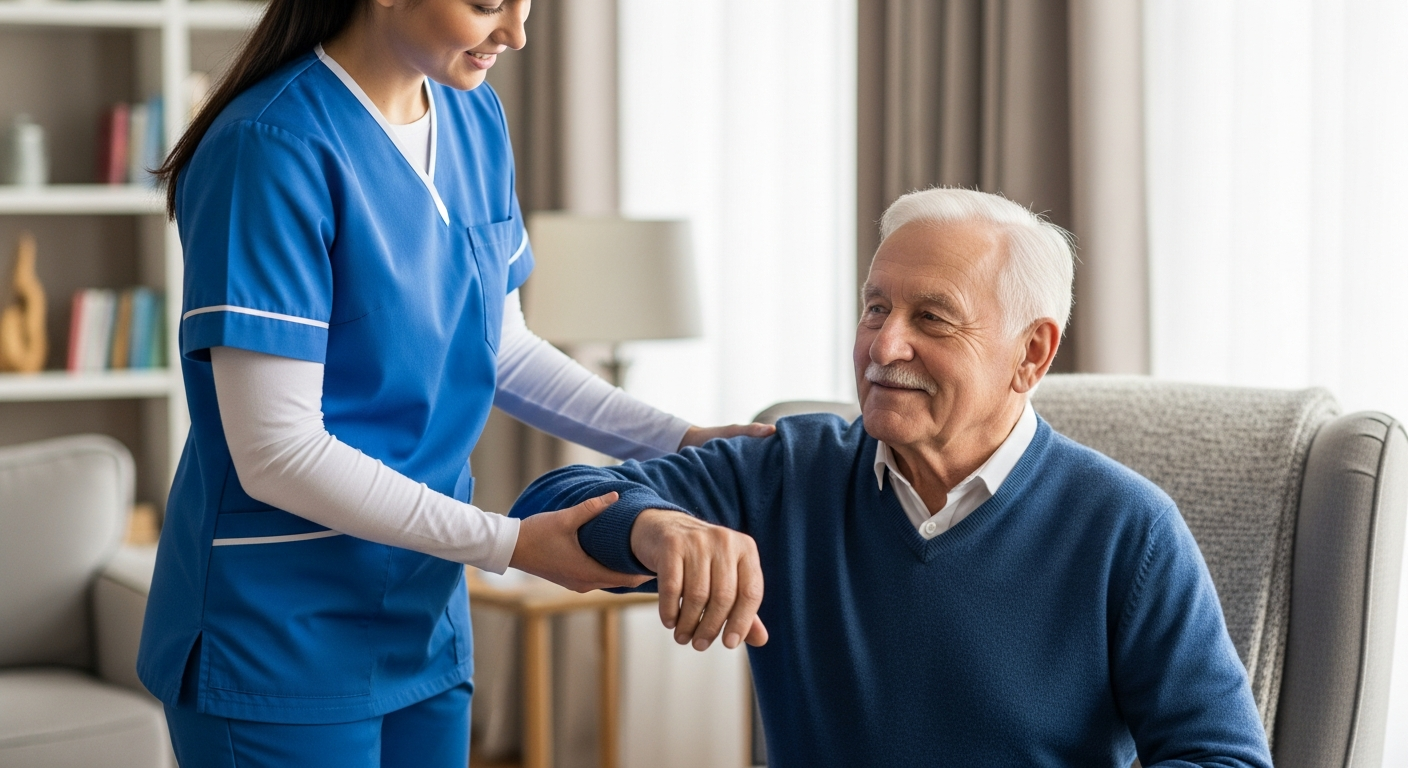

Australia’s aged care sector continues to grow as the population ages, creating ongoing demand for skilled caregivers who can provide compassionate, professional support to those in need. Caregivers work in various settings including residential aged care facilities, community care programs, and private homes, delivering essential services that help maintain quality of life for vulnerable individuals.
What are the primary caregiver responsibilities?
Caregivers perform diverse duties that extend far beyond basic assistance. Personal care forms a significant component, including help with bathing, dressing, grooming, and mobility support. Medication management is another critical responsibility, ensuring individuals take prescribed medications correctly and on schedule. Caregivers also assist with meal preparation, considering dietary requirements and nutritional needs specific to each person’s health condition.
Domestic support tasks such as light housekeeping, laundry, and maintaining a clean, safe living environment fall within the caregiver’s remit. Emotional and social support represents an equally important aspect, as caregivers often become trusted companions who help combat isolation and loneliness. Documentation of care provided, monitoring health changes, and communicating with healthcare professionals and family members are administrative responsibilities that ensure continuity of care.
Understanding the caregiving role overview in Australian aged care
The caregiving profession in Australia operates within a structured framework that emphasizes person-centred care. This approach recognizes each individual’s unique needs, preferences, and life history, tailoring support accordingly. Caregivers must balance respecting independence while providing necessary assistance, promoting dignity and autonomy wherever possible.
Working hours can vary significantly, with positions available across day shifts, night shifts, and weekend rotations. Some caregivers work full-time in residential facilities, while others provide flexible community-based care. The role demands physical stamina, as it often involves assisting with transfers, supporting mobility, and spending considerable time on one’s feet. Emotional resilience is equally important, as caregivers regularly encounter challenging situations and must maintain professional boundaries while demonstrating genuine compassion.
How aged care services Australia structure support delivery
Aged care services in Australia operate under government regulation and quality standards designed to protect vulnerable individuals. The Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission oversees service providers, ensuring compliance with the Aged Care Quality Standards. These standards cover areas including consumer dignity and choice, ongoing assessment and planning, personal care and clinical care, services and supports for daily living, organization’s service environment, feedback and complaints, and human resources.
Services are typically divided into residential aged care, where individuals live in purpose-built facilities, and home care packages, which enable people to receive support while remaining in their own homes. Community care programs also provide day centres, respite care, and specialized services for conditions such as dementia. Caregivers work within multidisciplinary teams alongside registered nurses, allied health professionals, and care coordinators to deliver comprehensive support.
Essential caregiving skills and duties for effective support
Successful caregivers possess a combination of technical skills and personal attributes. Practical skills include proper manual handling techniques to prevent injury when assisting with mobility, basic first aid knowledge, and understanding of infection control procedures. Observation skills enable caregivers to notice subtle changes in health status, behaviour, or mood that may indicate developing problems.
Communication skills are fundamental, particularly when working with individuals who have hearing impairments, cognitive decline, or language differences. Patience, empathy, and cultural sensitivity help build trusting relationships. Time management and organizational abilities ensure all required tasks are completed efficiently without compromising care quality. Problem-solving skills allow caregivers to adapt to unexpected situations and respond appropriately to emergencies.
Qualifications and pathways for support roles in aged care
Entering the caregiving profession in Australia typically requires formal qualifications. The Certificate III in Individual Support (Ageing, Home and Community) is the standard entry-level qualification, covering essential knowledge and practical skills for working in aged care settings. This nationally recognized qualification can be completed through registered training organizations, often combining classroom learning with workplace experience.
Some positions may accept Certificate III in Individual Support (Disability) or equivalent qualifications. Additional specialized training may be required for specific roles, such as dementia care or palliative care support. Many employers provide ongoing professional development opportunities, and career progression pathways exist for those who wish to advance into senior caregiver roles, team leadership positions, or pursue nursing qualifications.
Background checks including police checks and working with vulnerable people checks are mandatory for all aged care workers. First aid and CPR certification is typically required or provided during employment. Understanding of the Aged Care Quality Standards and relevant legislation forms part of the training and ongoing compliance requirements.
Career considerations and workplace realities
Caregiving offers meaningful work with direct impact on people’s lives, providing personal satisfaction that comes from helping others. The profession offers flexibility in working arrangements and employment settings, accommodating various lifestyle needs. However, the role can be physically demanding and emotionally challenging, requiring strong self-care practices and support networks.
The aged care sector faces workforce challenges including staff shortages in some regions, which can create opportunities but also workplace pressures. Conditions and remuneration vary between employers, with enterprise agreements and awards governing employment terms in many organizations. Those considering caregiving careers should research different employers, understand their rights and entitlements, and consider whether the role aligns with their personal capabilities and career goals.
Caregiving in Australia represents a vital profession that will continue growing in importance as demographic trends drive increased demand for aged care services. Those entering this field contribute meaningfully to society while developing valuable skills and building rewarding careers centred on compassion and professional care delivery.